The Hidden Dangers of Chronic Inflammation: How It Affects Your Body and What You Can Do About It
Inflammation is a natural defense mechanism ŌĆö your body’s way of fighting off infections, healing injuries, and protecting itself. In small doses and for short periods, acute inflammation is essential. But when inflammation becomes chronic, lingering for months or even years, it quietly undermines your health, often without noticeable symptoms until major problems emerge.
Chronic inflammation has been linked to a wide range of modern diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, cancer, AlzheimerŌĆÖs, autoimmune disorders, and even depression. Understanding this ŌĆ£silent fireŌĆØ is critical to maintaining long-term health and preventing disease.
ŌĆ£Beat the Pressure: A Comprehensive Guide to Lowering Blood Pressure Naturally.ŌĆØ
Buy book from Gumroad or Paystack
¤öź What Is Chronic Inflammation?
Inflammation is your immune systemŌĆÖs response to harmful stimuli ŌĆö such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. When you’re injured or infected, white blood cells rush to the site to protect and repair. You may experience redness, swelling, pain, or heat ŌĆö signs of acute inflammation.
However, chronic inflammation occurs when this response doesnŌĆÖt shut off. Instead, the immune system stays active, attacking healthy tissues and organs, mistaking them for threats. Over time, this leads to tissue damage and contributes to the onset of many serious illnesses.
¤¦¼ What Causes Chronic Inflammation?
Several factors contribute to chronic inflammation:
- Poor diet (high sugar, processed foods, trans fats)
- Chronic stress
- Environmental toxins
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Smoking and excessive alcohol
- Sleep deprivation
- Persistent infections
- Autoimmune conditions (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, lupus)
ŌÜĀ’ĖÅ Health Conditions Linked to Chronic Inflammation
1. Heart Disease
Chronic inflammation damages blood vessels, promotes plaque buildup, and increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Inflammatory markers interfere with insulin signaling, leading to insulin resistance and eventual diabetes.
3. Cancer
Inflammation can cause DNA damage and promote the growth of malignant cells, especially in cancers like colon, liver, and breast cancer.
4. AlzheimerŌĆÖs Disease
Neuroinflammation is now believed to be a major contributing factor to AlzheimerŌĆÖs and other neurodegenerative conditions.
5. Autoimmune Disorders
Conditions like lupus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis are all fueled by inflammation, as the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue.
6. Obesity
Excess fat, especially visceral fat, produces pro-inflammatory cytokines, keeping the body in a state of low-grade inflammation.
7. Digestive Disorders
Conditions like inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), CrohnŌĆÖs disease, and ulcerative colitis involve ongoing inflammation of the gut.
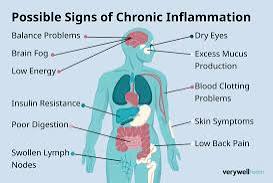
¤ö¼ Common Signs of Chronic Inflammation
While chronic inflammation often develops silently, you may notice:
- Fatigue
- Joint or muscle pain
- Brain fog
- Digestive issues (bloating, constipation, or diarrhea)
- Frequent infections
- Skin problems (acne, eczema, psoriasis)
- Unexplained weight gain or weight loss
Ō£ģ How to Reduce and Prevent Chronic Inflammation
Fortunately, chronic inflammation is not irreversible. Through targeted lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce inflammation and boost your bodyŌĆÖs resilience.
¤ŹĮ’ĖÅ 1. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
- Eat more omega-3-rich foods: salmon, flaxseeds, walnuts.
- Increase antioxidant intake: berries, leafy greens, colorful fruits.
- Use anti-inflammatory herbs and spices: turmeric, ginger, garlic.
- Avoid refined carbs, sugar, and processed foods.
- Choose whole grains over white flour products.
- Stay hydrated with water and green tea.
¤¦ś 2. Manage Stress
Chronic stress releases cortisol, which fuels inflammation. Practice:
- Meditation
- Deep breathing
- Mindfulness
- Journaling
- Counseling or therapy when needed
¤øī 3. Get Quality Sleep
Aim for 7ŌĆō9 hours of restorative sleep nightly. Sleep helps regulate the immune system and prevent inflammation.
¤ÜČ 4. Exercise Regularly
Moderate, consistent activity helps lower inflammatory markers.
- Brisk walking
- Swimming
- Yoga
- Resistance training
Even 30 minutes a day makes a significant difference.
¤ÜŁ 5. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Both significantly increase inflammation and damage your bodyŌĆÖs repair systems.
¤¦¬ 6. Monitor Your Inflammation
Your doctor can test for inflammation using:
- CRP (C-reactive protein)
- ESR (Erythrocyte sedimentation rate)
- Cytokine levels
Discuss these tests if you have ongoing health concerns or family history of inflammatory conditions.
¤ī┐ Natural Supplements That May Help
- Turmeric (curcumin)
- Fish oil (EPA and DHA)
- Resveratrol
- Quercetin
- Boswellia
- Vitamin D
ŌÜĀ’ĖÅ Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements.
¤¦Ā Final Thoughts
Chronic inflammation is often called the ŌĆ£root of all diseaseŌĆØ, and rightfully so. It silently degrades the bodyŌĆÖs systems and accelerates aging and illness. The good news? You have powerful tools at your disposal to fight back ŌĆö through food, movement, sleep, and stress management.
By making inflammation-lowering choices every day, you donŌĆÖt just prevent disease ŌĆö you enhance energy, boost longevity, and reclaim vibrant health.
┬Ā
¤Æö ŌĆ£She said she loved me. And for fifty-two years, I believed her.ŌĆØ ¤Æö
Buy The Book "The Longest Lie: A HusbandŌĆÖs Journey Through Love, Betrayal, and Redemption" From Gumroad
┬Ā






